I. Introduction to Common Rail Fuel Injection
Piezoelectric injectors have become a staple in commercial vehicle engines. Among the leading models, Siemens piezoelectric diesel injectors—also commonly referred to as Continental Injectors, Siemens VDO Injectors, or simply Siemens Injectors—stand out for their advanced design and performance. This guide explores their technology, applications, and key advantages in modern diesel systems.
II. Background on Piezo Injector Technology
Bosch vs. Siemens: A Technological Shift
- Bosch’s Early Piezo Innovation: In late 2005, Bosch introduced piezoelectric ceramic injectors, replacing traditional solenoid valves. Key improvements included:
- Reduced moving parts from 4 to 1, cutting mass by 75%
- 50% faster switching time than solenoid injectors
- 160 MPa injection pressure with 0.1 ms response time
- Capability for 5 injections per cycle
- 4th-Generation Common Rail Systems: The latest systems reach 250 MPa pressure with gradual ramping, ditching piezoelectric ceramics for hydraulic servo injectors with hydraulic amplification. This shift prioritizes durability and precision under extreme pressure.
Siemens’ Piezo Leadership
Siemens VDO, now under the Continental brand umbrella, was an early adopter of piezo technology. The injectors, whether labeled as Siemens VDO Injectors or Continental Injectors, maintain their reputation for quality:
- PCR2 System (2nd Generation): 165 MPa pressure, 5 injections per cycle
- PCR3 System (3rd Generation, 2006): 180 MPa pressure, meeting Euro V standards without a particulate filter
- Real-World Application: Used in JAC Navistar MaxxForce engines in China, these injectors—recognized by various names like Siemens piezoelectric diesel injectors or Continental Injectors—prove their reliability in the field.
III. Understanding Piezoelectric Ceramics
01 What Are Piezoelectric Ceramics?
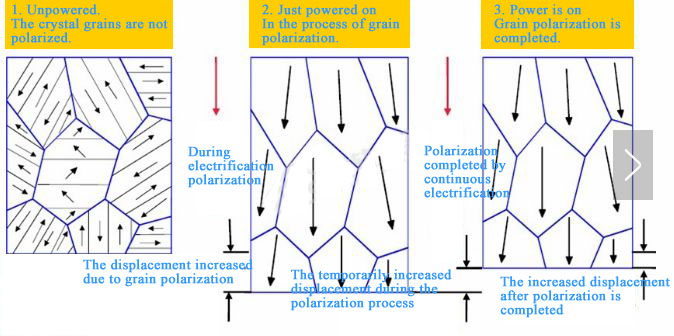
Ceramics are polycrystalline materials made from sintered powders. Piezoelectric ceramics are specially processed to have a “piezoelectric effect”:
- Manufactured via high-temperature sintering, machining, silver electrode coating, and DC voltage polarization
- Named for production processes similar to traditional ceramics
02 The Piezoelectric Effect Explained
Applying mechanical force to certain materials causes charge polarization, generating opposite charges on surfaces. In Siemens piezoelectric diesel injectors (or Continental Injectors, Siemens VDO Injectors), this means:
- Piezo crystals deform when voltage is applied
- Ceramic piezoelectric films distort within 0.1 microseconds of energization
- 30mm actuators use 300+ layers of 80μm-thick films for sufficient displacement
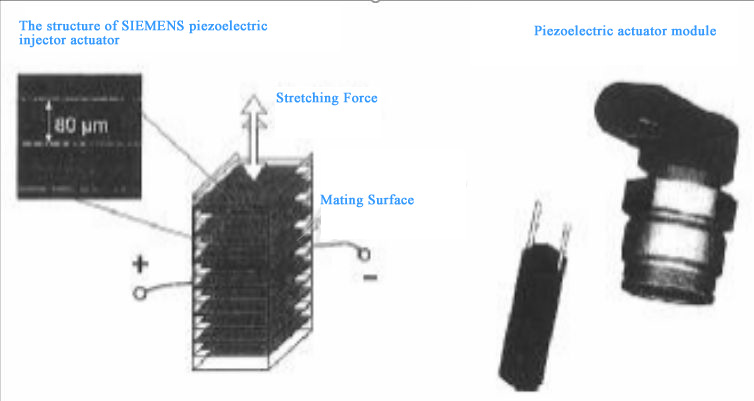
03 Why Use Piezo Crystals in Injectors?
Key requirements for automotive piezo crystals in Siemens VDO Injectors and similar models like Continental Injectors:
- Temperature range: -40°C to +150°C
- High strength; 100–200V operation
- Lift: 1/1000 of thickness; 30 microsecond switching time
- Durability: Over 10^9 cycles
Benefits for common rail systems:
- Better fuel atomization (finer droplets)
- 5% power increase; 20% emission reduction
- 3% fuel savings; 3dB(A) noise reduction
- Smaller size than electromagnetic injectors
- Precise control over fuel quantity, timing, and pressure
IV. Siemens Piezoelectric Diesel Injectors Structure
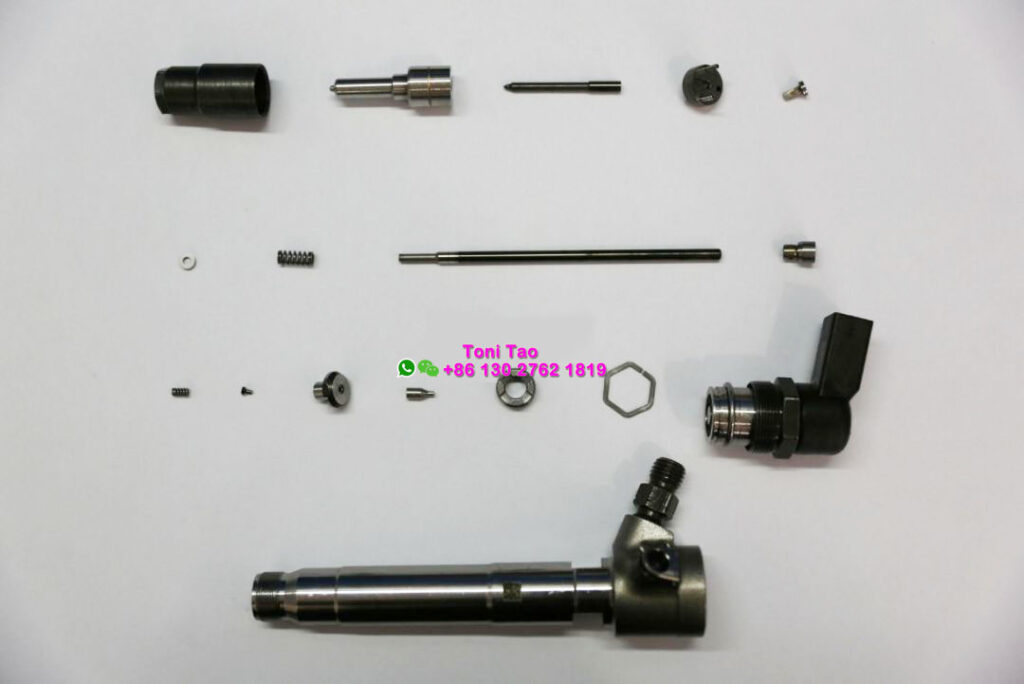

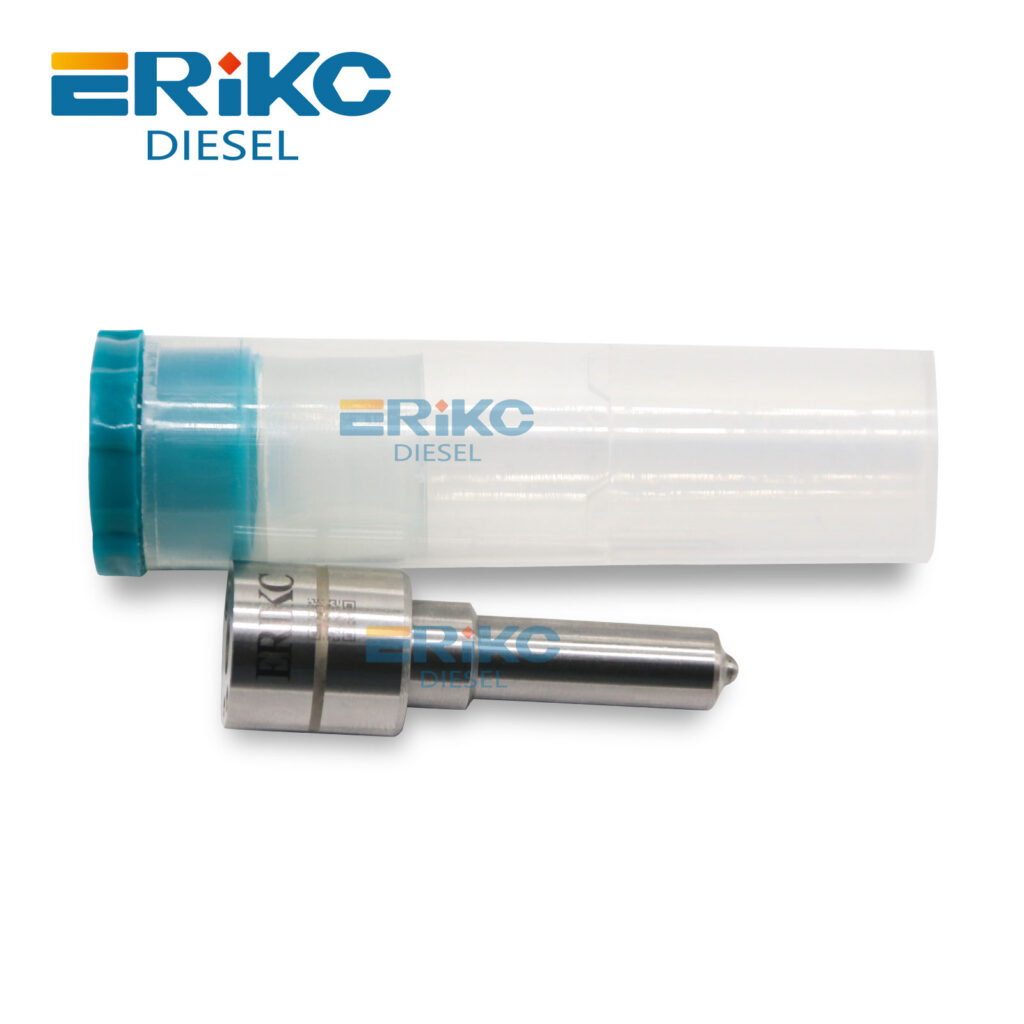
01 Nozzle Assembly

Key design features applicable across Siemens, Siemens VDO(Continental) injectors:
- Sunken Nozzle Design: Nozzle needle and body sit at different planes, with 230μm lift (sinking distance)
- Separator(Plunger Guide) & Pressure Push Rod(Nozzle Plunger):
- Separator(Plunger Guide) protects nozzle from high-pressure oil erosion
- Push rod(Nozzle Plunger) conducts force and allows leakage backflow to return channels

02 Valve Assembly
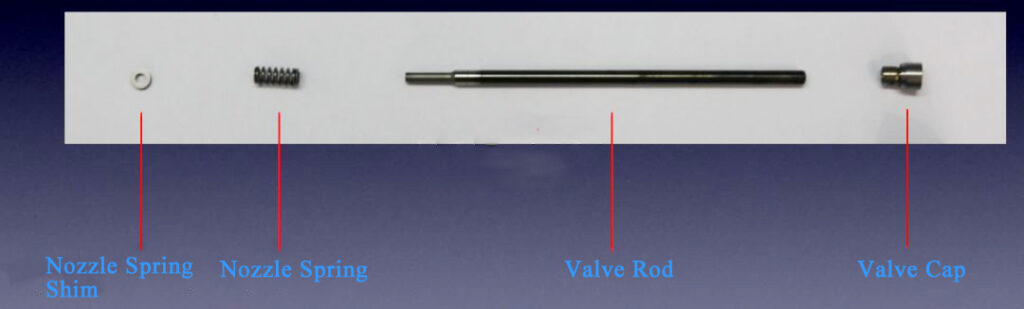
Similar to traditional injectors but with a smaller valve cap for compactness, a feature consistent across Siemens piezoelectric diesel injectors and their branded variants like Continental Injectors.
03 Mushroom Valve Part
The core difference from traditional injectors, regardless of branding:
- Replaces armature with piezo crystal actuation
- Piezo deformation (amplified by a lever) moves the control valve piston and mushroom valve
- Opens the high-pressure control chamber for injection

V. Working Principle of Siemens Piezo Injectors
01 Power Off State
- High-pressure fuel enters the control chamber and nozzle
- Mushroom valve closes the return port via spring force
- Larger control piston area keeps the nozzle closed due to higher hydraulic force (F2)
02 Powered On State
- Piezo actuator pushes the valve piston (via lever), opening the return port
- Reduced control chamber pressure makes F2 exceed F1 (force on piston)
- Nozzle needle lifts, injecting fuel through 5 holes
- Minimal fuel leakage lubricates the needle guide
| Power – On Time | 540 | 540 | 460 | 230 | 520 |
| Rail Pressure | 1500 | 1500 | 800 | 1200 | 250 |
| Standard Fuel Quantity | 37.2 | 33.2 | 19.7 | 6.4 | 5.9 |
| Maximum | 60 | 39.7 | 24 | 9.3 | 8.6 |
| Minimum | 10 | 26.7 | 15.4 | 3.4 | 3.2 |
Performance Advantages
- Faster opening allows short intervals between pre-injection and main injection
- Enables smoother combustion and lower noise
- Significantly faster response than hydraulic injectors

VI. Disassembly and Assembly Guide
01 Tools Needed
- Torque wrench, 15mm box wrench, special tools, 26/27mm open-end wrench

02 Disassembly Steps
- Nozzle Part:
- Remove nozzle nut, nozzle, separator(plunger guide), push rod(nozzle plunger), nozzle spring, and nozzle spring shim with 15mm wrench

- Solenoid Part:
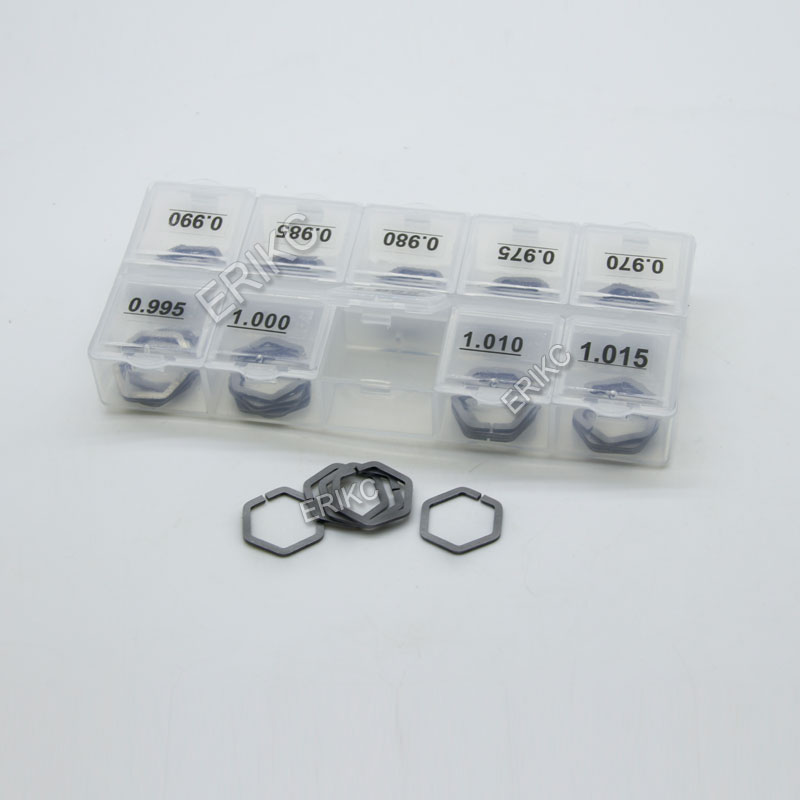
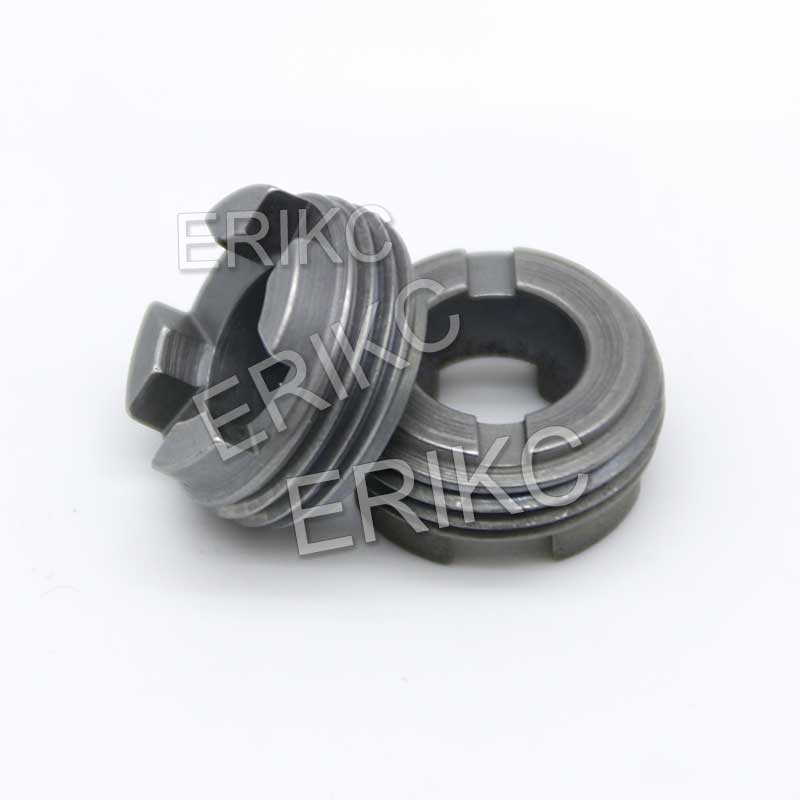
- Unscrew solenoid(actuator) with 27mm wrench; remove solenoid(actuator), driving valve pin(control valve piston) and hexagonal shim(solenoid/actuator shim)

- Locking Screw:
- Use special tools to remove screw, control valve, mushroom valve, return spring(valve spring), and stem(valve rod)

03 Assembly Steps
- Control Valve Part:
- Install the valve stem(valve rod), return spring(valve spring), mushroom valve, control valve, and locking screw(screw nut) in sequence according to the disassembly order, and tighten the locking screw to a torque of 65Nm.
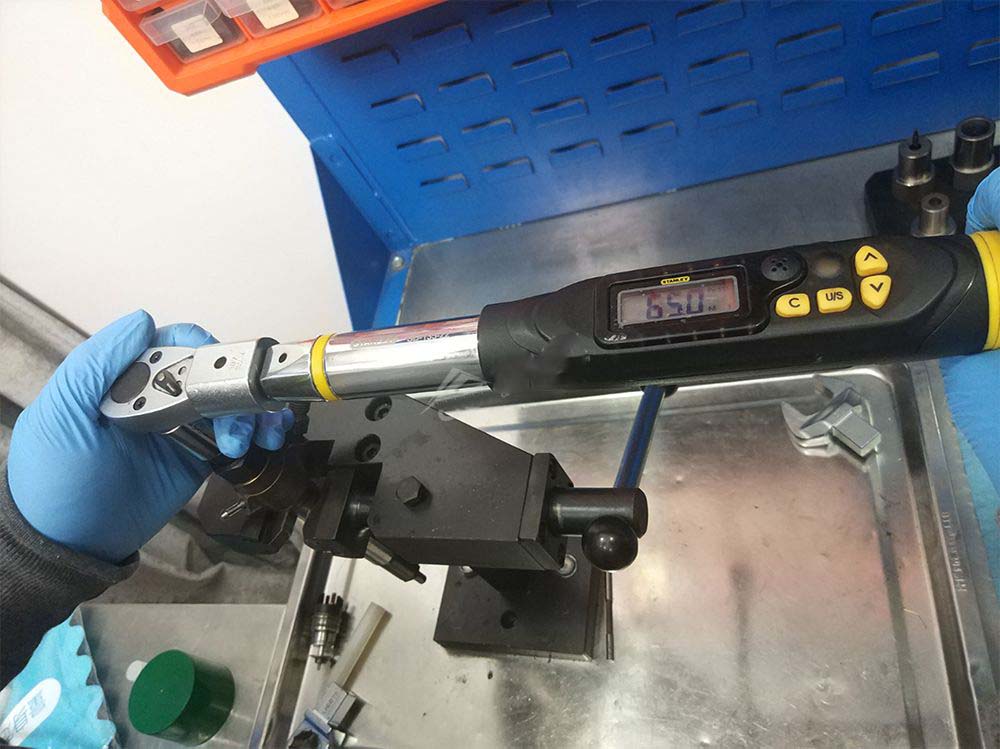

- Install the valve stem(valve rod), return spring(valve spring), mushroom valve, control valve, and locking screw(screw nut) in sequence according to the disassembly order, and tighten the locking screw to a torque of 65Nm.
- Solenoid Valve Part:
- Put in the control valve piston(driving valve pin), hexagonal shim(solenoid valve shim), and solenoid valve(actuator) in sequence, and tighten the solenoid valve retaining nut to a torque of 25Nm.
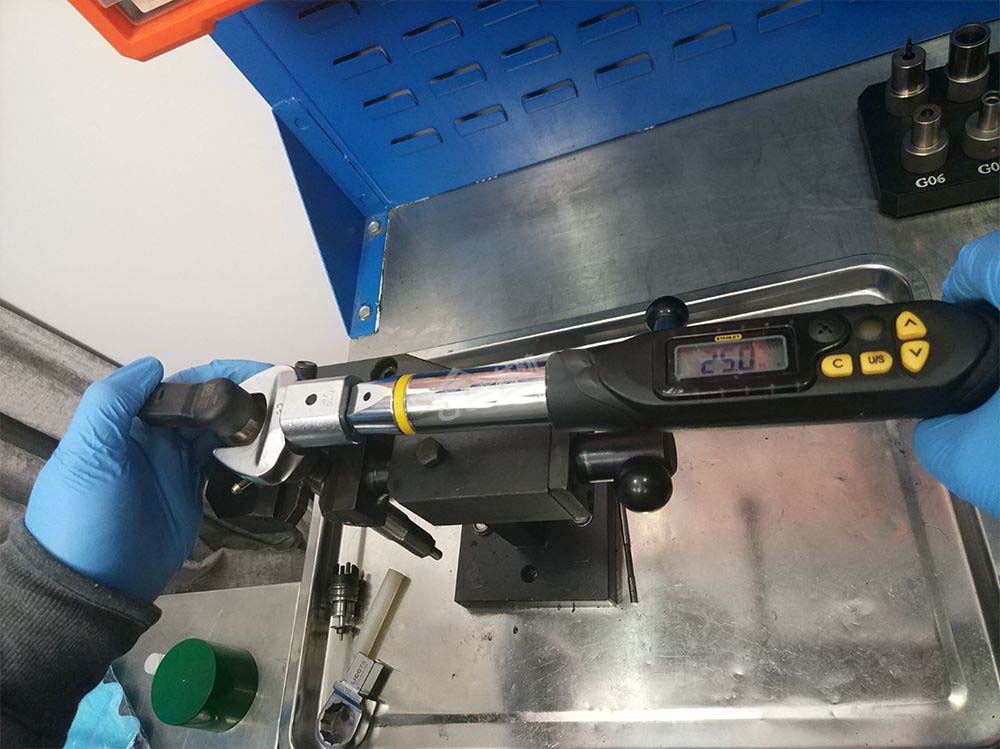

- Put in the control valve piston(driving valve pin), hexagonal shim(solenoid valve shim), and solenoid valve(actuator) in sequence, and tighten the solenoid valve retaining nut to a torque of 25Nm.
- Nozzle Part:
- Install the nozzle spring shim, nozzle spring, pressure push rod(nozzle plunger), separator(plunger guide), nozzle, and nozzle retaining nut in sequence, and tighten the nozzle retaining nut to a torque of 60Nm.
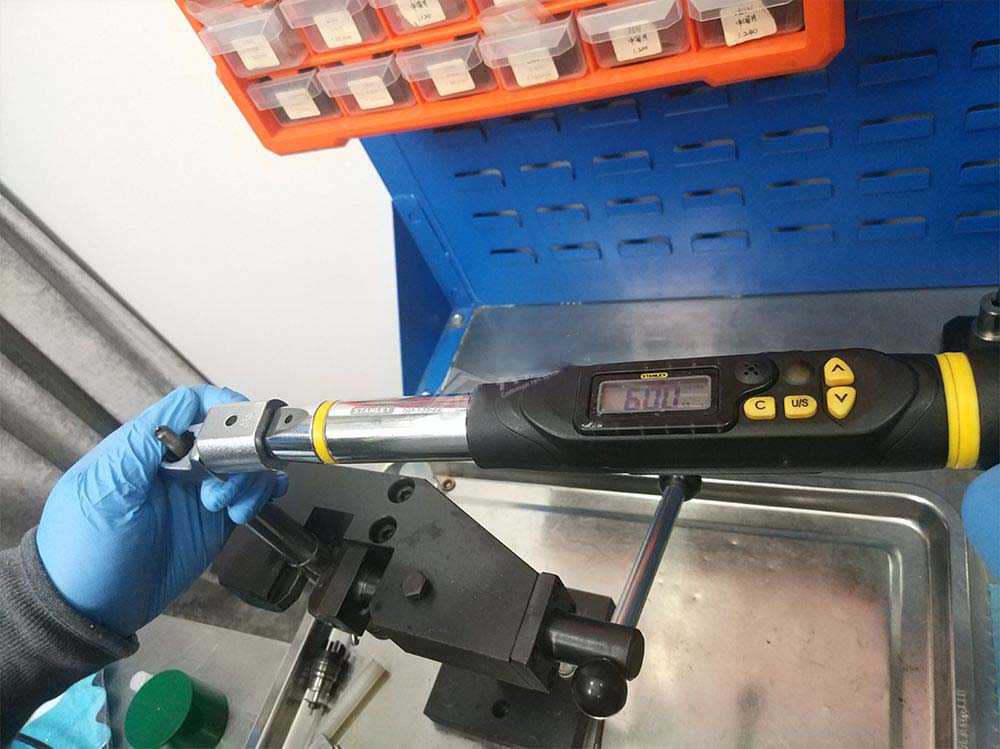

- Install the nozzle spring shim, nozzle spring, pressure push rod(nozzle plunger), separator(plunger guide), nozzle, and nozzle retaining nut in sequence, and tighten the nozzle retaining nut to a torque of 60Nm.
🔧 Recommended Alternatives from ERIKC Diesel
If you’re a diesel workshop, injector remanufacturer, or distributor looking for reliable replacements for Siemens piezoelectric injectors, ERIKC provides:
- 🔧 Small MOQ & bulk availability
- 🚚 Fast delivery from stock
- 🧾 OEM code cross-reference support
- 🌍 Worldwide shipping















❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
🔹1: What are common signs of Siemens piezo injector failure?
A: Typical symptoms include:
- Poor fuel economy
- Increased emissions
- Misfiring or rough idling
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Injector open circuit fault codes
🔹 Q2: What tools do I need to service Siemens piezoelectric injectors?
A: You’ll need:
- Torque wrench
- 15mm and 26/27mm open-end wrenches
- Piezo disassembly tools
- Cleanroom-grade workspace to avoid contamination
🔹 Q3: Do ERIKC replacement parts affect ECU programming?
A: No. ERIKC mechanical parts like valve rods, nozzles, and spacers do not interfere with ECU programming. However, injector coding (e.g., IQA or QR codes) may still be needed if replacing the full injector.

