An engine with one or more cylinders not functioning properly is often referred to as “misfiring.” Misfires may involve a single cylinder or multiple cylinders. They are typically associated with issues in the ignition system, fuel injection system, or cylinder pressure. Misfiring occurs when combustion is incomplete or fails altogether. Let’s explore the reasons behind misfires and how to identify them.
Why Misfires Happen
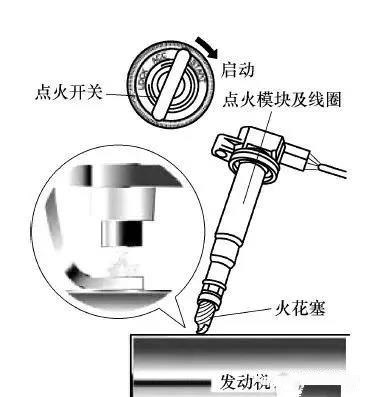
For an engine to operate properly, it needs the right combination of fuel, cylinder pressure, and spark. During operation, the ignition coil delivers a 2-3 kV voltage to the spark plug for ignition. Meanwhile, the fuel system supplies fuel to the injector, and cylinder pressure relies on the proper sealing of the cylinder walls and spark plug. If any of these components fail, a misfire can occur, triggering a fault code in the engine control unit (ECU).
Consequences and Symptoms of Misfires
When misfires occur, the following symptoms and issues may arise:
- Engine Vibration: The engine may run rough or vibrate abnormally.
- Reduced Power: The engine’s performance drops, and it struggles to deliver power.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Incomplete combustion leads to higher fuel consumption.
- Catalytic Converter Damage: Unburned fuel can enter the exhaust system and damage the catalytic converter.
Severe misfires can cause the engine to vibrate significantly, and some vehicles may experience “popping” sounds during acceleration due to combustion in the exhaust pipe. Additionally, unusual noises, such as “chugging” from the exhaust, may be observed. In such cases, the vehicle is likely to fail emissions testing.

How to Detect Misfires
There are several ways to diagnose misfires, commonly involving diagnostic tools or manual inspection methods:
Using a Diagnostic Tool
- Connect a diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s system.
- Access the engine control system and select the data stream.
- Check the misfire rate for each cylinder. Under normal conditions, the misfire rate should be zero.
Using the Cylinder Interruption Method
If a diagnostic tool is unavailable, the cylinder interruption method can be used:
- Disconnect the diesel injector plug for each cylinder one at a time.
- Observe engine RPM changes. If disconnecting a particular diesel injector does not significantly affect RPM, that cylinder likely has a fault.
Next Steps After Identifying a Faulty Cylinder
Once the problematic cylinder is identified, the following areas should be inspected:
- Ignition System:
- Check the ignition coil and spark plug.
- Inspect the spark plug gap, carbon buildup, and signs of damage or electrical leakage.
- Fuel System:
- Examine the diesel injector for clogs or malfunctions.
- Cylinder Pressure:
- Test the cylinder compression to ensure it meets specifications.
- Timing System:
- Inspect the timing mechanism to ensure proper alignment and check for timing belt or chain slippage.
Summary
Misfires can be identified using fault codes via diagnostic tools or the cylinder interruption method. The main causes of misfires are typically found in the ignition system, fuel system, cylinder pressure, or engine timing. Proper diagnosis and maintenance of these components are essential to ensure optimal engine performance.

